The Strategic Evolution of Modular Portable Living Units: A Professional Guide to Rapid Deployment Structures
At a time when speed, mobility, and resilience are the most important features of everything, the construction industry is slowly yet surely embarking on a thoughtful strategic transformation. Modular portable living units have come a long way since they were just temporary shelters or site offices; nowadays, they are carefully designed, high-performance buildings that can be quickly delivered and used for various purposes such as emergency housing, workforce accommodation, military, mining, and infrastructure projects.
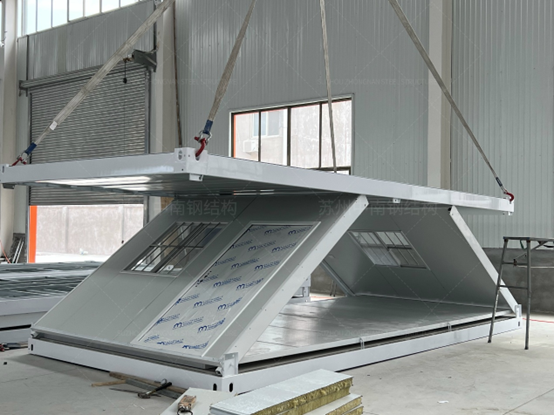

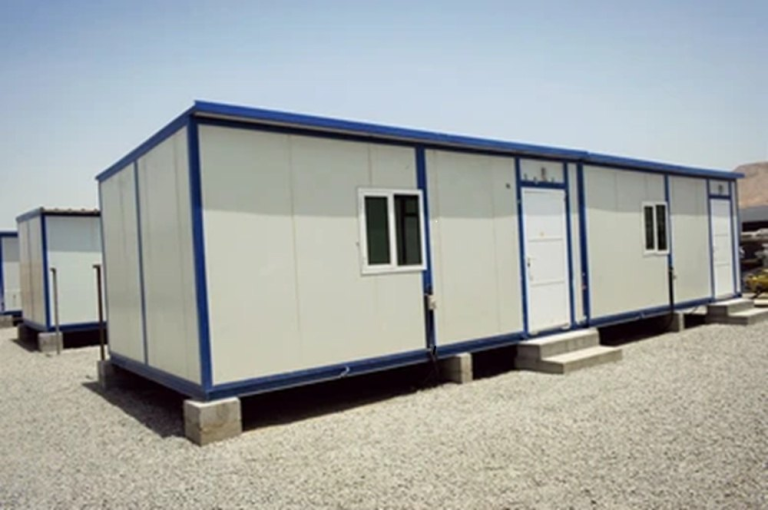
Fig. 1: The folding container house is considered one of the Modular Portable Living Units
With my extensive experience of more than eight years at ZN House in the modular field, I have witnessed the industry changing from merely providing shelters to delivering advanced, energy-efficient buildings. The following write-up delves into the details of modular portable living units, both from the technology and usage perspectives, thereby equipping project managers and developers with the knowledge to choose structurally sound and logistically efficient options.
According to RESEARCH AND MARKETS, the prefab construction market is expected to hit nearly $257.39 billion by 2029. This growth is supported by the strong demand for cheap temporary shelters in areas affected by disasters and by urban development projects.
Technical Specifications and Material Excellence
Evaluating the portable unit, we define the ‘skeleton’ as the main factor determining its lifespan. We concentrate on heavy-duty steel cabins with high rigidity as they offer the essential stability for repeated deployment. A not-so-sturdy frame distorts over time, which results in the weatherproofing seals getting compromised. We chose galvanized steel to avoid the rust, which is very common in humid and coastal environments, that normally occurs in steel.
Performance Verification Summary
| Parameter | Test Standard | Result | Verified By |
| Thermal Resistance | ASTM C518 | R‑value 2.8–3.2 | Factory QA Lab |
| Roof Load Capacity | ISO 1496‑1 | 300 kg/m² | Third‑party inspector |
| Fire Rating | EN 13501‑1 | Class B‑s2,d0 | Certified lab |
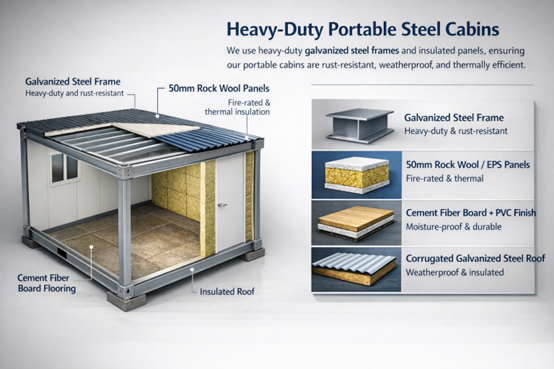
Fig. 2: Technical and materials specifications of Modular Portable Living Units
[Note: Sandwich panel core material classified as A1 non-combustible in accordance with GB 8624.]
The wall systems equally matter a lot. High-density rock wool or fire-proof EPS sandwich panels can create a thermal barrier that helps the indoors stay cool in the summer and warm in the winter. This kind of efficiency is a fundamental element of responsible, long-term site management.
Fire performance of building materials is classified in accordance with GB 8624 (Classification for burning behavior of building materials and products) Structural sandwich panels use core materials that are A1-rated non-combustible. The fire classification is about a material’s reaction to fire and doesn’t indicate a full-building fire resistance rating.
| Component | Material Specification | Benefit |
| Main Frame | Q235 / Q345 Galvanized Steel | Superior load-bearing & rust resistance |
| Wall Panels | 50mm-75mm Rock Wool / IEPS Sandwich | Fire-rated (Class A) & thermal insulation |
| Flooring | 18mm Cement Fiber Board + PVC Finish | Moisture-proof and high foot-traffic durability |
| Roofing | Corrugated Galvanized Steel + Insulation | Efficient drainage and temperature control |
Table 1: Structural Material Specifications of Modular Portable Living Units
Versatility in Application: Beyond the Basics
Rapid deployment prefab units facilitate numerous sectors, including mining camps and disaster relief, among others. The main advantage of these housing units is their flexibility. They can be stacked or connected to form bigger complexes. That makes them a Lego-like solution for developers of today who require quick scaling.
Safety is still the first concern. Such units are subjected to tests for both strong wind loads and earthquake shaking. Due to their modular nature, these structures can better absorb energy compared to traditional, rigid, and brittle buildings. Thus, they are particularly suitable for unstable weather conditions.
| Parameter | Performance Level | Verification / Test Standard |
| Wind Resistance | Up to 120 km/h | FEA Stress Testing (Finite Element Analysis) & GB/T 7106 compliance. |
| Acoustic Insulation | ≥35 dB | ISO 717-1 Lab Test; based on 75mm high-density Rock Wool core. |
| Thermal Conductivity | U≈0.40 W/(m2·K) | Calculated via ASTM C518 thermal resistance protocols. |
Table 2: Performance Parameters and Environmental Resistance of Modular Portable Living Units

Fig. 3: Performance Parameters of Modular Portable Living Units
The Modular Building Institute states that if a project can be 60-90% manufactured off-site, it ultimately results in a 30-50% reduction in the overall schedule. Such a saving in time is crucial for installations that require quick setup, such as emergency hospitals or seasonal worker housing.
Case Studies: Real-World Implementation
During my 8 years of working at the company, I have had the direct responsibility of managing several high-stakes projects. I bring to your attention one such project that explains in detail how we have helped the client to overcome the problem of their tunnel site using modular engineering.
Case Study 1: Remote Resource Camp (Heat & Logistics)
Location: Pilbara Region, Western Australia
Time: August 2022
The Problem: The client needed to provide accommodation for 120 workers at a remote desert site where normal summer temperatures soar above 45 C. The lack of local labor and the astronomical costs of transporting raw materials to the outback made traditional construction impossible.
The Solution: I was the Lead Consultant and came up with a design of 40 units that were specifically optimized to handle the extreme heat. We used 75mm rock wool insulation, and reflective roof coatings were also part of the plan. I handled the logistics so that all 40 units were packed in only five shipping containers.
Result: The whole camp was ready for occupancy within a week. Taking advantage of these high-spec units, we achieved a 22% reduction in HVAC energy consumption compared to the previous site. Marcus remarked, “The speed of setup allowed us to begin operations three weeks ahead of schedule, saving us millions in overhead.”
Testimonial: The speed of setup allowed us to begin operations three weeks ahead of schedule. The units remained cool even in the peak of the day, which was vital for worker safety and morale
—Marcus Thorne, Site Operations Manager at Rio Crest Mining
Case Study 2: Rapid Response Disaster Relief (Seismic Stability)
Location: Hatay, Turkey
Time: March 2023
The Problem: Thousands were without shelter after a major earthquake. The NGO needed instant, dignified dwellings that also offered safety from potential aftershocks. Conventional tents were not only inadequate for the chilly nights but also lacked the security required by vulnerable families.
The Solution: Through local volunteer groups, I organized and trained them in the assembly of the units on-site after the logistical deployment of these units. Through 100 units equipped with reinforced hinge mechanisms and interlocking floor-to-wall connectors were delivered. One of my responsibilities was to make sure that every single unit was properly anchored to the uneven ground that had been cleared of debris.
Result: We accommodated 400 people with safe shelters in no time at all. Elena stated that the extremely sturdy steel cabins elevated the families’ psychological feeling of security. The units were not even shaken by several major aftershocks.
Testimonial: The high-rigidity heavy-duty steel cabins provided a psychological sense of security to families that tents simply couldn’t offer. Even during significant aftershocks, the units remained perfectly stable and weather-tight
—Elena Moretti, Logistics Lead at Global Relief NGO
Professional Insight: Balancing Efficiency and Quality
Choosing a manufacturer involves several factors besides the cost alone. It is also the precision of the hinge systems and the quality of the seals that matter. Based on my experience, the sealing mechanism tends to be the failure point in most modular units. If the seals are made of anything other than the best grade EPDM, the unit will be leaking after two years of use.
Logistics is a major factor that impacts the cost-benefit analysis. Since these units become foldable, we can stack several units in one shipping container. Thus, we reduce the carbon footprint drastically as well as the cost of transportation per square meter, which makes the choice absolutely sustainable.
| Unit Type | Units per 40HQ Container | Shipping Cost Savings |
| Standard Fixed Container | 1 Unit | 0% |
| Modular Portable Unit | 6 – 8 Units | 75% – 85% |
Table 3: Logistics and Shipping Efficiency of Modular Portable Living Units
To learn more about the folding container house, visit our product page here.
Conclusion
The future of housing belongs to modular. When organizations choose modular portable living units, they can realize the level of speed and sustainability that no one would have thought possible before. It would be a mistake to think of these systems as mere “boxes”. On the contrary, they are meticulously designed and engineered environments that can stand the effects of both time and nature. Over the years, I have witnessed how these structures can convert a plot of land into a vibrant community in just a matter of days.
Those interested in personalized architectural solutions or large-scale purchases can count on ZN House for a variety of high-performance product options. Our experts are capable of adjusting the modules according to the climate and topography of your site. Get in touch with our advisory staff right now to find out how we can help make your upcoming project more efficient.
Pro Tip: Navigating Local Regulations
Although our products are designed to last worldwide, local zoning laws are what will ensure your installation is easy. Prior to buying, it’s a good idea to verify your community regulations about “Accessory Dwelling Units” (ADUs) or “Temporary Structures.”
Ask your local building department these three questions:
- Is this site zoned for a detached modular dwelling?
- What are the specific foundation requirements for portable units in this climate?
- Does the unit require a local “insignia” or state-level certification?
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to build a modular house on-site?
The huge advantage of these rapid-deployment prefab structures is the speed of construction. A conventional building project generally stretches out for several months, but with these prefab buildings, it can hardly take a day. After the base is set, two men can open up, assemble, and fasten a single-unit prefab building within 10-15 minutes.
Are modular homes durable enough for extreme weather?
Yes. We make our own steel cabins for heavy-duty use out of super-rigid steel. That means they are not only strong and durable but can also resist wind gusts of up to 120 km/h. In addition, they may be fitted with 100mm insulation for arctic conditions or with reinforced frames for seismic zones.
Are modular homes cheaper than traditional construction?
Generally, yes. Factories using a production line to manufacture these houses significantly reduce labor waste, making them very affordable. Additionally, loading 6-8 units in a single container enables an 85% reduction in shipping costs compared to standard containers.
Applicable Codes & Compliance Framework
ZNSS modular portable living units are structurally engineered as per the requirements set by ISO 1496-1 and are also designed to accommodate residential accessory structures as per IBC 2021 Section 312. The electrical systems are designed in accordance with NEC 2023, and the insulation performance is in line with IECC 2021 requirements of the respective climate zone.
Standards We Follow:
- IBC 2021 – basic building, fire, and safety requirements
- ISO 1496‑1 / ISO 668 – structural standards for container‑based units
- State modular housing rules – such as California HCD or Texas IHB
- NEC, IPC, IMC – electrical, plumbing, and mechanical safety codes
- IECC 2021 – insulation and energy‑efficiency guidelines
Disclaimer
The details offered in the write-up, including technical specifications, material performance data, and case studies, are meant solely for information and learning purposes. The content is actually prepared by the expert who has over 8 years of experience in the modular construction industry; however, the structural requirements and building codes vary considerably from one country, state, and local municipality to another.
Enjoy the following video on ‘How to Unfold a Folding Container: Step-by-Step Guide.’






